Peds ID Abx QOTW #14 Answer
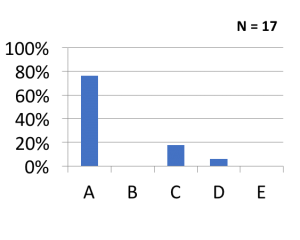
A) Unasyn
C) Ceftriaxone
Here’s how others answered:
Acute Mastoiditis
- Most common infecting organisms include
- S. pneumoniae
- S. pyogenes (GAS)
- S. aureus
- Symptoms include the following:
- Intense otalgia, retroauricular swelling, and a protruding ear caused by subperiosteal abscess formation
- Commonly preceded by an acute otitis media
- Antibiotic treatment has not been proven to prevent mastoiditis
- Diagnosis is based on clinical exam, not radiologic exam
Management of Acute Mastoiditis
- Antibiotic choice
- Recommendations include Amp/sulbactam (Unasyn) or Amox/Clav (Augmentin) or 3rd generation cephalosporin (Ceftriaxone)
- No need to cover for Pseudomonas unless growing out of culture
- More common in patients with tympanostomy tubes and in recurrent AOM
- Can consider antipseudomonal coverage in these situations (Cefepime or Zosyn)
- Levofloxacin should not be used except in severe PCN allergy
- Rates of MRSA are very low in acute cases of mastoiditis
- In other words, empiric vancomycin is not necessary
- Surgical management usually required
- Myringotomy tubes
- Drainage of abscess
Discussion of this case
- The initial outpatient management was correct
- Augmentin was a good choice, and he already had started to drain via a perforation
- His failure was not because of incorrect outpatient antibiotic selection for this patient
- This patient needed surgical drainage for management
- Early surgical consult should be done
- Continuation of Amp/Sulb (Unasyn) or ceftriaxone would have be the best options listed