ECG 4
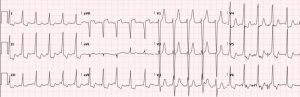
A patient with WPW and orthodromic supraventricular tachycardia, such as this patient, will often be indistinguishable from other SVTs, and will have a regular narrow QRS tachycardia. AV nodal blockers such as adenosine and verapamil are OK in these patients.
WPW patients with antidromic tachycardia have wide QRS complexes, resembling ventricular tachycardia, and are treated with amiodarone or procainamide or cardioversion.
WPW patients with atrial fibrillation will have an irregular very fast tachycardia, with QRS of varying morphology – avoid AV nodal blockers such as adenosine, Ca channel blockers including verapamil, beta blockers, digoxin, and amiodarone in these patients, as blocking the orthodromic pathway may result in excessive impulses down the accessory pathway leading to ventricular fibrillation. Go straight to cardioversion in this case.
This is an excellent review of pharmacology and WPW patients
After adenosine treatment, the patient’s ECG looked like this: